From the workstation of Nigel R. A. Beeley, CDD Advocate
In This Article:
Ever since the musings of A. V. Hill (1) over 100 years ago which produced what is now known as the Hill-Langmuir equation (2) to describe pharmacological observations (the contractile effects of nicotine on the frog rectus-abdominis muscle, elaborated upon later with the O2 Hemoglobin system) as bimolecular interactions which followed the law of mass action, the dose-response curve has been a fundamental feature of both pharmacology and drug discovery and development.
Dose-Response Curve Definition
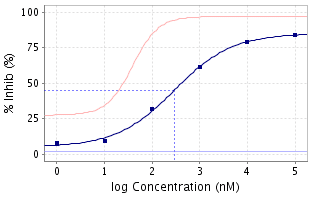
The dose-repsonse curve is typically semi-logarithmic with the X-axis being the logarithm of the concentration or dose and the Y axis being response, usually measured as a percentage of some baseline value. The curve can be either ascending (agonists, enhancers) or descending (antagonists, inverse agonists) and should ideally be sigmoidal. Mixed agonist/antagonist molecules can deliver bell-shaped dose response curves.
Applications of the Dose-Response Curve
Key values such as the concentrations EC50 and IC50 can be read directly off the curve by constructing an intersecting vertical and horizontal line at the point of 50% response. Application of the Hill-Langmuir equation to such curves reveals the Hill coefficient, nH which can, in turn, lead to better understanding of the binding modes of ligands (3).
More recent variants include the Gaddum equation (4) (allows for two ligands interacting with the biological system) and the Schild plot (5) (a log/log plot which can distinguish by curve shape between non-competitive, competitive and cooperative binding, heterogeneous receptors and failure to reach equilibrium).
Benefits of the Dose-Response Curve
It wasn’t too long ago that medicinal chemists working in a multidisciplinary drug discovery team would be presented with a simple number (the EC50 or IC50) by their pharmacological counterparts as an indicator of biological activity. Indeed, medicinal chemistry publications typically continue to report structure-activity relationships (SARs) in tabular forms using such numbers. The benefits of seeing the full data set behind the computed numbers, the cornerstone of today’s pharmacology/chemistry interface, were lost to parts of the team.
The advent of fully integrated database systems, such as the offerings of CDD Vault, provide multiple opportunities for examination of the details of dose response curves. Simply eyeballing the screening plate in a color coded format can provide instant feedback regarding quality, the inadvertent “sneeze” over the plate, the “drool” of the over-zealous operator, being immediately obvious.
The curves themselves oftentimes can immediately raise comfort or caution, the sudden drop-off or enhancement in the curve compared to the ideal sigmoidal shape, the presence of a “straight line” even though the computer has produced a sigmoidal fit, the failure to reach an expected maximal response at high concentrations, etc. etc. all of which lead to more questions than answers that are typically followed up with repeat experiments.
The modern database calculates curves on the fly which also allows for dose response curve manipulations, such as removing an obvious outlier from the curve calculation (NOT from the data set), to see how the curve changes. All in all, for 90 years the musings of A. V. Hill and his successors have been largely hidden away from parts of multidisciplinary drug discovery and development teams (6) … over the past 15 years integrated databases have changed that forever for the better.
FAQs About Dose-Response Curves
These questions and answers will provide more detailed information about dose-response curves and their importance.
What is a dose-response curve?
A dose-response curve visually represents how a drug or substance affects an organism based on its concentration or dose. Typically, it shows the relationship between drug dosage (X-axis) and the biological response (Y-axis), which can be crucial in assessing efficacy and potency.
How do you make a dose-response curve?
To create a dose-response curve, plot the concentration or dose of a drug against the observed response. This often involves log-transforming doses to generate a sigmoidal curve, allowing clear interpretation of potency values like EC50 and IC50.
What is the Hill equation in dose-response curves?
The Hill equation models the sigmoidal shape of dose-response curves by describing how drug binding influences response. It provides insight into cooperativity among binding sites, revealing valuable data about binding strength and drug action mechanisms.
Why is a dose-response curve important?
Dose-response curves help researchers determine the optimal drug dose for desired effects, minimizing side effects. They allow scientists to compare compounds and their efficacies, crucial in drug discovery and development.
What is the difference between dose-response and drug-response curves?
A dose-response curve generally refers to any substance's effects based on dose, while a drug-response curve specifically describes pharmaceutical compounds' biological effects, focusing on therapeutic responses in drug development.
Let CDD Help You Implement Dose-Response Curves
All in all, for 90 years the musings of A. V. Hill and his successors have been largely hidden away from parts of multidisciplinary drug discovery and development teams (6) … over the past 15 years integrated databases have changed that forever for the better. Let CDD help you put dose-response curves to work for you. Contact us today to find out more.
References:
- Hill, A. V. (1910-01-22). "The possible effects of the aggregation of the molecules of hæmoglobin on its dissociation curves". Physiol. 40 (Suppl): iv–vii.
- Langmuir, Irving (June 1918). "The Adsorption of Gases on Plane Surface of Glass, Mica and Platinum". The Research Laboratory of The General Electric Company: 1361–1402
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hill_equation_(biochemistry)
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Receptor_theory
- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Schild_regression
- Rang HP (2006). "The receptor concept: pharmacology's big idea". J. Pharmacol. 147 (S1): S9–16.
This blog is authored by members of the CDD Vault community. CDD Vault is a hosted drug discovery informatics platform that securely manages both private and external biological and chemical data. It provides core functionality including chemical registration, structure activity relationship, chemical inventory, and electronic lab notebook capabilities.
CDD Vault: Drug Discovery Informatics your whole project team will embrace
Other posts you might be interested in
View All Posts
Events
11 min
March 27, 2025
Collaborative Drug Discovery's Inaugural Canadian User Group Meeting
Read More
CDD Blog
5 min
March 21, 2025
Drug Discovery Informatics for Big Pharma: Key Webinar Insights
Read More
CDD Vault Updates
3 min
March 19, 2025
CDD Vault Update (March #2 2025): Macromolecule Atomistic Rendering, AI Datasets, Import Inventory Locations, Larger Inventory Boxes, Dark Mode
Read More


